The processing technique of controlling roughness by controlling cutting parameters for materials of different hardness
The surface roughness of the workpiece
Roughness refers to the unevenness of a solid surface, describing the degree of fluctuation on the surface morphology and irregularity in the lattice structure
Cutting parameters
Cutting parameters collectively refer to the various motion parameters during cutting, including cutting speed, feed rate, and cutting depth
Cutting speed
It's the instantaneous speed of a point on the cutting edge of the tool relative to the workpiece surface in the primary motion direction
Feed rate
The relative displacement between the workpiece or tool in the feed direction for each revolution of the workpiece or tool. Depending on the feed direction, it's divided into longitudinal feed and transverse feed. Longitudinal feed refers to the feed along the direction of the lathe bed guide rail, while transverse feed refers to the feed perpendicular to the direction of the lathe bed guide rail.
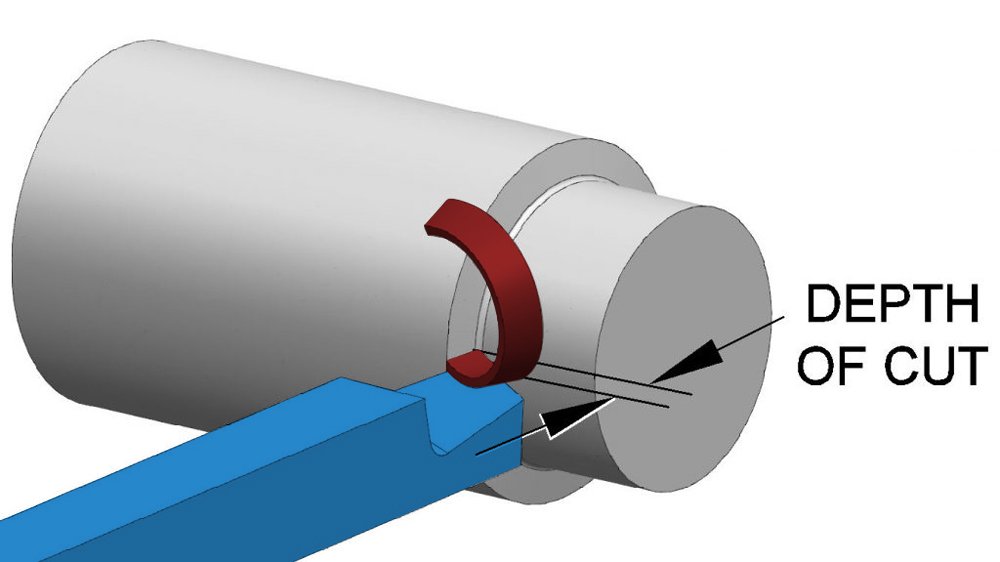
Cutting depth
The vertical distance between the machined surface and the surface yet to be machined during the cutting process.
In metal turning processes, the surface roughness of metal is influenced by numerous variables. Today, we're discussing how surface roughness is affected by different cutting parameters for metals of varying hardness when other variables remain constant.
The relationship between metal hardness and surface roughness
Generally speaking, under the same cutting parameters, the higher the hardness of the metal, the greater the cutting resistance generated on the surface of the metal during cutting, leading to more severe deformation before being cut off, resulting in greater surface roughness.
The relationship between cutting speed and surface roughness
In the case of the same metal material, without generating overheating or resonance phenomena during processing, the higher the cutting speed, the lower the surface roughness. This is because during the cutting process, the metal particles spend less time in the cutting area, which reduces cutting force and temperature. Lower cutting force and temperature can reduce the deformation of the metal surface and vibration in the cutting area, thereby helping to decrease surface roughness.
However, if the cutting speed is too high, it can also lead to increased friction between the cutting tool and the workpiece, resulting in higher temperatures and exacerbated tool wear. This can also lead to an increase in surface roughness. Therefore, adjustment of cutting speed is done within a limited range.
The relationship between feed rate and surface roughness
In the same material processing scenario, with other parameters held constant, increasing the feed rate results in a greater distance traveled by the cutting tool per unit time. This may lead to an increase in cutting forces and temperatures during the cutting process, causing greater deformation of the metal surface and increased vibration in the cutting area. Consequently, this leads to a larger surface roughness. In summary, the relationship between feed rate and surface roughness is typically positive; an increase in feed rate tends to result in an increase in surface roughness.
The relationship between cutting depth and surface roughness
In the case of the same metal and with all other machining parameters held constant, there is a positive correlation between cutting depth and surface roughness. This is because higher cutting depths can lead to increased cutting forces, temperatures, and material deformation, thereby resulting in greater surface irregularities and roughness.
In conclusion, when dealing with metals of higher hardness, it is advisable to use more durable cutting tools. Additionally, to reduce surface roughness, smaller feed rates, higher cutting speeds, and lower cutting depths are recommended. It's also important to implement effective cooling measures during the machining process to prevent overheating.