Turning vs Milling: What’s the Difference?
What is turning?
Turning is the process of modifying the blank's size and shape to match the specifications of the drawing by utilizing the workpiece's rotating motion and the linear or curved motion of the tool on the lathe.
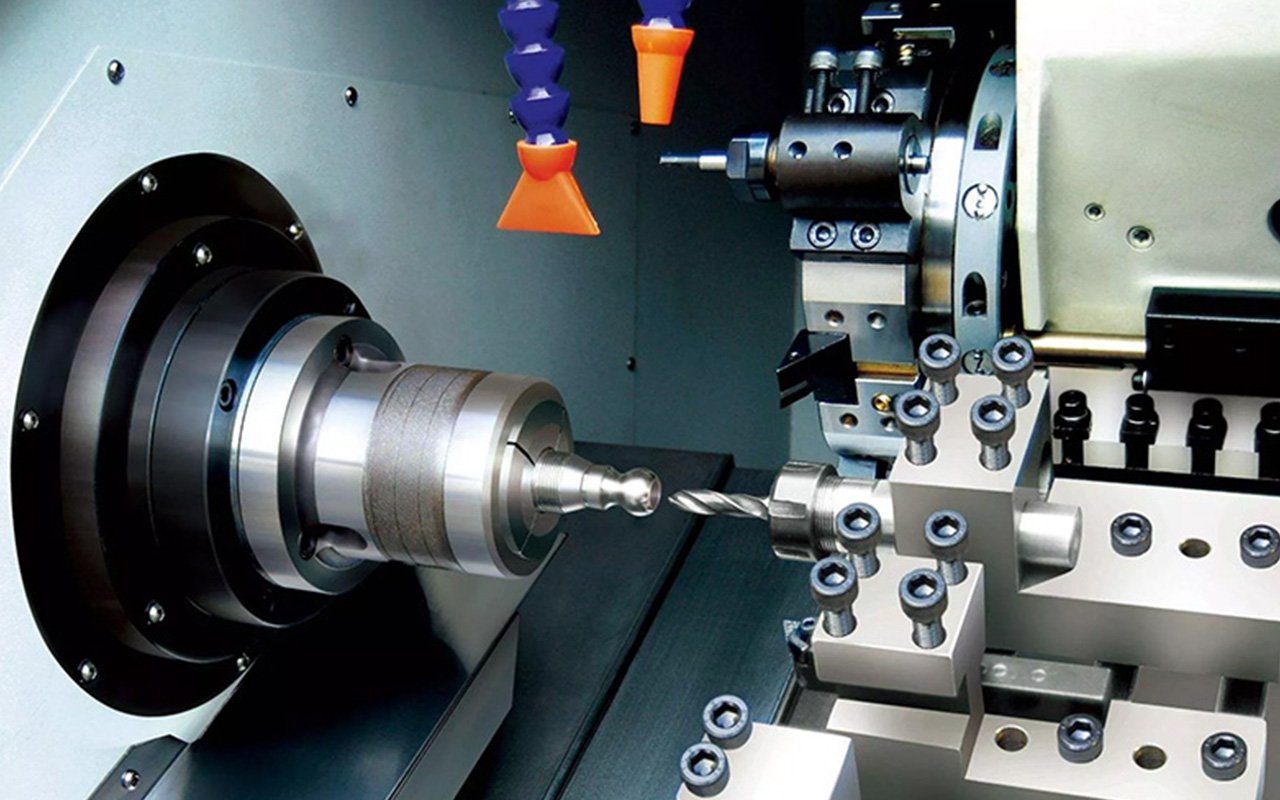
Turning is the process of employing the workpiece's rotation in relation to the tool to cut it on a lathe. Rather than the tool, the workpiece provides the majority of the cutting energy during turning. The most fundamental and widely used cutting technique, turning holds a significant place in the manufacturing process. Machining a rotating surface can be done by turning. The majority of workpieces with rotating surfaces, including end faces, grooves, threads, internal and external cylindrical surfaces, internal and external conical surfaces, and rotary forming surfaces, can be machined using the turning technique.
The lathe, which makes up almost half of all machine tools, is the most often used type of metal cutting machine. In addition to turning workpieces with lathe tools, the lathe can also be used for drilling, reamer, tapping thread, and hob operations. Lathes can be classified as horizontal lathes, landing lathes, vertical lathes, turret lathes, and profiling lathes, the majority of which are horizontal lathes, based on the various process features, layout forms, and structural qualities.
What is milling?
Complicated rotational body shapes can be processed using CNC lathes. The process of milling involves fixing the blank and using a high-speed, rotating milling cutter to cut off the necessary form and features. Conventional milling is mostly utilized for milling basic shape elements like grooves and contours. Complex features and shapes can be processed by a CNC milling machine. Three-axis or multi-axis milling and boring can be performed on processes, molds, fixtures, tread, thin-walled complicated surfaces, artificial prostheses, blades, and other items using a milling and boring machining center. When choosing NC milling material, it is important to fully utilize the advantages and crucial role of the NC milling machine.
In contrast to turning, a common cold working method for metal involves the tool rotating at a high speed while the workpiece remains mostly stationary due to the spindle. What separates milling from turning: The rotary pieces are processed by turning. Via the three-grasp chuck, the parts are secured onto the machine tool's main shaft and rapidly turned. Next, the product shape is cut out using the lathe tool in accordance with the rotary body's generatrix. The lathe can also be used for low speed processing with internal hole, thread, and bite flower processing.
Difference between Turning and Milling
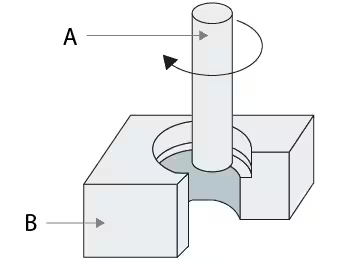
To put it simply: lathes are round, milling machines are flat. In lathe operations, the cutter is stationary while the workpiece rotates. The workpiece does not revolve during milling machine processing; instead, the tool rotates.
The lathe is a type of machine tool used mostly for turning workpieces. For equivalent processing, drills, reamers, taps, dies, and knurling tools can also be used on the lathe. The lathe is the most commonly used machine tool in factories that manufacture and repair machinery. It is primarily used for machining shafts, discs, sleeves, and other workpieces with spinning surfaces. Lathes are the foundation for all rotating machinery, including milling and drilling equipment. In Hong Kong and other Chinese regions, there are also individuals referred to as "rotary beds." A milling machine is a type of machine tool used primarily to machine different surfaces of workpieces using milling cutters.
Typically, the workpiece (and) milling cutter movement constitutes the feed motion, while the milling cutter's rotating motion is the primary motion. It can process different curved surfaces, gears, planes, and grooves. Using milling cutters, a milling machine is a type of machine tool. Milling machines are employed extensively in the manufacture and service departments of machinery because they can handle more complex profiles more efficiently than planers, in addition to milling planes, grooves, gear teeth, threads, and splined shafts.
A milling machine is a commonly used machine tool that can process a variety of curved surfaces, spiral surfaces (threads, spiral grooves), gear parts (gears, spline shafts, sprockets), and planes (horizontal and vertical planes). It can also be used for cutting off, milling, and other tasks involving the rotating body's inner hole and surface. When the milling machine is operating, the workpiece is mounted on the worktable or any accessories like the indexing head. The milling cutter rotates as the primary movement, with the worktable or milling head's feeding movement serving as a supplement to enable the workpiece to receive the necessary machined surface.
Because it involves intermittent cutting with many cutters, the milling machine's productivity is increased. a piece of machinery used to mill objects using a milling cutter. Milling machines are employed extensively in the manufacture and service departments of machinery because they can handle more complex profiles more efficiently than planers, in addition to milling planes, grooves, gear teeth, threads, and splined shafts. The term numerical control is inserted before its name, automatic processing, and refers to two different types of machine tools that are programmed to follow the knife path.